Have you ever wondered how your body functions so seamlessly? From the rhythmic beat of your heart to the intricate network of nerves sending signals at lightning speed, the human body is a masterpiece of design. It consists of organs, bones, muscles, and tissues, all working in perfect harmony to keep you alive.
In this in-depth guide, we’ll explore the body systems that make up this fascinating structure. You’ll discover the skeletal system that provides stability, the nervous system that controls everything, and even lesser-known organs that play vital roles in human physiology. Whether you’re a student, a health enthusiast, or just curious about your own anatomy, this article will break it all down in simple terms.
Understanding the Human Body
The Complexity of Human Anatomy
The human body isn’t just a collection of organs and bones—it’s an intricate system of interconnected parts working together in perfect sync. Think of it like a giant biological machine where every tiny component has a purpose.
From the moment you’re born, your body grows, adapts, and constantly repairs itself. Right now, millions of cells inside you are busy regenerating, ensuring your tissues stay healthy. Even when you’re asleep, your organs keep functioning—your heart keeps pumping, your lungs keep breathing, and your brain keeps processing information.
Mind-Blowing Facts About the Human Body
- Your brain generates enough electricity to power a small lightbulb.
- Your heart beats around 100,000 times a day—that’s nearly 35 million times a year!
- Your bones are five times stronger than steel but light enough to allow easy movement.
- Your skin sheds nearly 40,000 cells every minute—yet, it remains your body’s largest organ!
With such an incredible system at play, understanding how it all works isn’t just fascinating—it’s essential for your well-being.
The Importance of Knowing Your Body Parts
Why should you care about body anatomy? Because knowledge is power—quite literally! Understanding how your organs function helps you make better choices for your health and spot signs when something’s wrong.
Imagine feeling fatigued all the time. If you know that the thyroid gland controls your metabolism, you might realize that a thyroid imbalance could be the culprit. Or if you’re experiencing chronic joint pain, understanding the skeletal system might help you pinpoint the issue.
How This Knowledge Benefits You
Helps in early disease detection
Improves posture and movement
Boosts overall health awareness
Aids in making informed medical decisions
Your body is the most valuable asset you have. The more you understand it, the better you can take care of it.
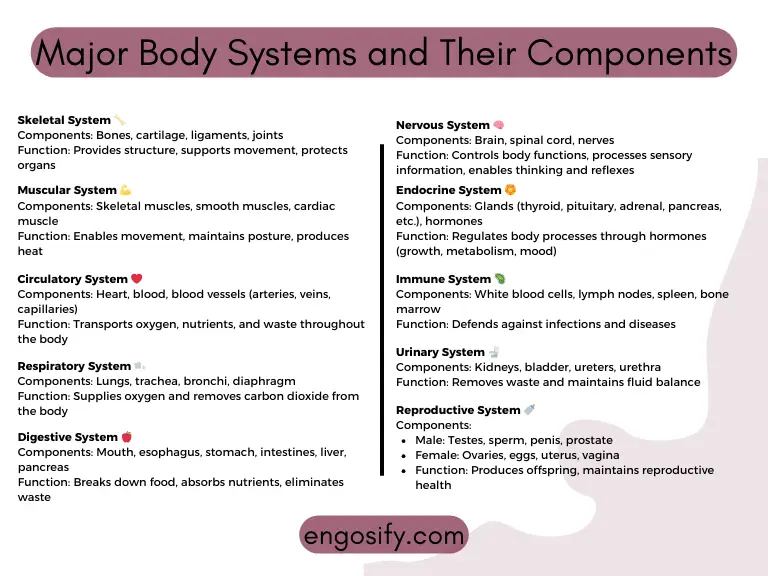
Major Body Systems and Their Components
The human body is like a bustling city—each system acts as a department, ensuring everything runs smoothly. Without these body systems, survival would be impossible! From breathing and digestion to movement and blood circulation, each one plays a crucial role in keeping you alive.
Now, let’s dive into the major body systems, breaking them down into their essential organs and functions.
1. Integumentary System
The integumentary system is your first line of defense—it’s what you see when you look in the mirror! This system includes your skin, hair, and nails, working together to protect your internal organs from harm.
Skin: The Body’s Largest Organ
- Shields your body from infections, UV rays, and dehydration
- Regulates body temperature through sweating
- Contains sensory receptors that allow you to feel touch, pain, and temperature
Hair: More Than Just a Style Statement
- Helps regulate body temperature
- Provides a layer of protection (eyelashes keep debris out of your eyes!)
- Contains keratin, the same protein that strengthens nails
Nails: Built-in Defense Mechanism
- Protects fingertips from injury
- Aids in gripping small objects
- Reflects overall health—brittle nails can indicate nutrient deficiencies
2. Musculoskeletal System
Want to run, jump, or even blink? That’s all thanks to the musculoskeletal system—your bones, muscles, and joints working together to give you movement and stability.
Bones: The Framework of Your Body
Your skeleton consists of 206 bones, giving structure and protection to vital organs. Some key functions include:
- Supporting your body’s weight
- Protecting delicate organs (e.g., the skull shields the brain)
- Producing blood cells in the bone marrow
Muscles: The Powerhouse of Motion
Did you know your body has over 600 muscles? These muscles are responsible for voluntary movements (like waving) and involuntary movements (like your heart beating).
Types of Muscles:
- Skeletal muscles – Help in movement (e.g., biceps, quadriceps)
- Cardiac muscle – Found only in your heart, keeping it pumping
- Smooth muscles – Line your digestive tract and help with food movement
Joints: The Flexible Connectors
Without joints, movement would be impossible! They:
- Connect bones together
- Allow bending, twisting, and rotating movements
- Contain cartilage to reduce friction
3. Nervous System
The nervous system is your body’s command center, constantly processing information and sending out signals. It’s responsible for everything from thinking and memory to muscle coordination.
Brain: The Ultimate Control Center
- Controls thoughts, emotions, and movements
- Processes sensory information (what you see, hear, taste, etc.)
- Regulates involuntary actions like breathing and heartbeat
Spinal Cord: The Communication Highway
- Acts as a messenger, transmitting signals between the brain and body
- Enables reflex actions (like pulling your hand away from a hot stove)
- Protected by vertebrae to prevent injury
Nerves: The Body’s Wiring System
- Carry electrical signals throughout the body
- Control voluntary and involuntary movements
- Help detect pain, pressure, and temperature
4. Circulatory System
The circulatory system is the body’s transport network, ensuring that oxygen, nutrients, and hormones reach every cell while removing waste products.
Heart: The Lifelong Pump
Your heart beats 100,000 times a day, pumping oxygen-rich blood throughout your body. It has four chambers:
- Right atrium & right ventricle – Pump oxygen-poor blood to the lungs
- Left atrium & left ventricle – Pump oxygenated blood to the rest of the body
Blood Vessels: The Transport Routes
- Arteries – Carry oxygenated blood away from the heart
- Veins – Bring deoxygenated blood back to the heart
- Capillaries – Tiny vessels where gas exchange happens
Blood: The Essential Fluid
- Contains red blood cells (oxygen transport), white blood cells (immune defense), and platelets (clotting)
- Delivers nutrients to cells
- Removes carbon dioxide and other waste
👉 Want to learn more? Check out this detailed list of human anatomical features to explore every inch of your body!
5. Respiratory System
The respiratory system allows you to take in oxygen and expel carbon dioxide. Every time you breathe, this system ensures your cells get the oxygen they need!
Lungs: The Oxygen Hub
- Exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide through tiny air sacs called alveoli
- Expand and contract up to 20 times per minute
Trachea: The Windpipe
- Transports air from your nose/mouth to the lungs
- Lined with mucus to trap dust and germs
Diaphragm: The Breathing Muscle
- Contracts to pull air into the lungs
- Relaxes to push carbon dioxide out
6. Digestive System
Hungry? The digestive system ensures that your food is broken down into nutrients that fuel your body.
Mouth: Where Digestion Begins
- Teeth grind food
- Saliva starts breaking down carbohydrates
Esophagus: The Food Highway
- Pushes food into the stomach using muscle contractions
Stomach: The Acidic Blender
- Uses gastric acids to break down food
- Kills harmful bacteria
Intestines: The Absorption Zone
- Small intestine – Absorbs nutrients into the bloodstream
- Large intestine – Extracts water and forms waste
7. Excretory System
Your excretory system gets rid of waste products, ensuring that your body stays clean and toxin-free.
Kidneys: The Body’s Filters
- Remove waste from the blood
- Regulate hydration levels
Bladder: The Storage Tank
- Holds urine until it’s time to release it
8. Endocrine System
The endocrine system produces hormones, which control everything from growth to mood swings.
Glands and Their Functions
- Thyroid gland – Regulates metabolism
- Adrenal glands – Control stress response
- Pancreas – Manages blood sugar
9. Reproductive System
The reproductive system ensures the continuation of human life.
Male Reproductive Organs
- Testes – Produce sperm and testosterone
Female Reproductive Organs
- Ovaries – Release eggs and hormones
- Uterus – Supports fetal development
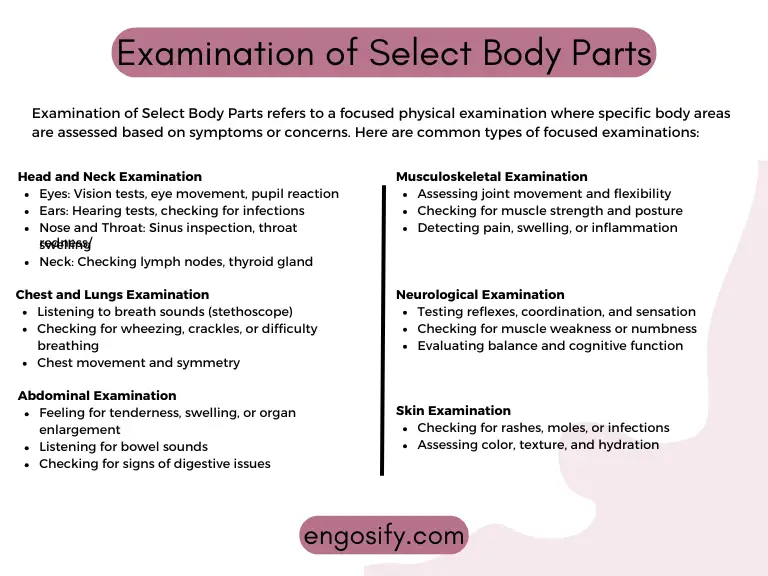
Detailed Examination of Select Body Parts
Now that we’ve covered the major body systems, let’s zoom in on some of the most important and fascinating organs in your body. These are the powerhouses that keep you moving, thinking, and functioning every single day!
1. The Human Heart: The Lifeline of the Body ❤️
Your heart is a relentless engine, pumping blood non-stop to keep your body alive. On average, it beats 100,000 times a day, sending oxygen-rich blood to every organ.
Anatomy of the Heart
Your heart is divided into four chambers:
- Right Atrium & Right Ventricle – Pump oxygen-poor blood to the lungs.
- Left Atrium & Left Ventricle – Pump oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body.
Between these chambers are valves that ensure blood flows in one direction—like a well-organized traffic system!
How the Heart Works
- Oxygen-poor blood enters the right atrium.
- It gets pumped to the lungs, where it picks up oxygen.
- Oxygen-rich blood then enters the left atrium and moves into the left ventricle.
- Finally, the left ventricle sends it out to nourish your entire body.
💡 Did You Know?
Your heart pumps about 2,000 gallons of blood daily—enough to fill a fire truck!
Learn more about how the heart functions here.
2. The Brain: The Ultimate Control Center 🧠
Your brain is the most powerful organ you own—it controls everything, from your thoughts and emotions to your breathing and heartbeat.
Main Regions of the Brain
- Cerebrum – The largest part, responsible for thinking, learning, and memory.
- Cerebellum – Controls balance and movement coordination.
- Brainstem – Regulates vital functions like breathing and heartbeat.
Mind-Blowing Brain Facts
- Your brain generates enough electricity to power a small lightbulb.
- It contains about 86 billion neurons—more than the number of stars in the Milky Way!
- Even though it makes up only 2% of your body weight, it uses 20% of your body’s energy.
🧠 Boost Your Brain Power:
Eating omega-3-rich foods (like salmon and walnuts) helps improve brain function!
3. The Liver: The Body’s Detox Machine
Your liver is like a chemical factory, breaking down toxins and helping with digestion, metabolism, and immunity. It’s the only organ in your body that can regenerate itself!
Key Functions of the Liver
Filters toxins – Removes harmful substances from the blood.
Produces bile – Helps digest fats and vitamins.
Stores energy – Regulates blood sugar levels.
💡 Cool Fact:
Your liver performs over 500 vital functions every single day!
4. The Skin: The Body’s Largest Organ
Your skin does way more than just cover your body—it’s a defense shield against germs, UV rays, and injuries.
Layers of the Skin
- Epidermis – The outermost layer, protecting against bacteria and toxins.
- Dermis – Contains sweat glands, nerve endings, and hair follicles.
- Hypodermis – The deepest layer, storing fat for insulation.
Why Your Skin Is Important
- It regulates temperature by releasing sweat.
- It detects pain and pressure through nerve endings.
- It repairs itself quickly—a minor cut can heal in just a few days!
💡 Did You Know?
Your skin renews itself every 27 days—so you’re constantly getting a new outer layer!
Lesser-Known But Essential Body Parts
Now that we’ve explored some of the most well-known organs, it’s time to shine a spotlight on lesser-known but equally vital body parts. You may not think about them often, but without these, your body wouldn’t function properly!
1. The Spleen: The Silent Protector
Your spleen may not get as much attention as your heart or brain, but it plays a crucial role in keeping your immune system strong.
Functions of the Spleen
🦠 Fights infections – Produces and stores white blood cells to attack bacteria and viruses.
🩸 Filters blood – Removes damaged red blood cells and recycles iron.
🔋 Stores emergency blood supply – Holds extra blood in case of injury or blood loss.
💡 Did You Know?
Your spleen can function even if a part of it is removed—your body adapts to compensate for the loss!
2. The Pancreas: The Sugar Regulator
You might associate the pancreas with digestion, but it does much more than just help break down food!
Why the Pancreas Matters
🍔 Produces digestive enzymes – Breaks down fats, proteins, and carbs.
🩸 Regulates blood sugar – Releases insulin and glucagon to keep glucose levels balanced.
⚠️ Health Alert!
When the pancreas doesn’t function properly, it can lead to diabetes—a condition where blood sugar levels become too high.
Learn more about how the pancreas regulates blood sugar here.
3. The Hypothalamus: The Body’s Thermostat
Ever wondered how your body temperature stays stable? That’s the job of the hypothalamus, a small but mighty part of your brain!
What the Hypothalamus Controls
🌡️ Body temperature – Keeps you from overheating or getting too cold.
😴 Sleep cycles – Regulates circadian rhythms (your body’s internal clock).
🍔 Hunger & thirst – Signals when you need food and water.
🧠 Mind-Blowing Fact:
Your hypothalamus is only about the size of an almond but controls nearly every automatic function in your body!
4. The Appendix: More Useful Than You Think!
For years, scientists thought the appendix was useless—but recent research suggests it has a role in gut health!
The Surprising Functions of the Appendix
🔬 Houses good bacteria – Helps restore gut bacteria after an infection.
🛡️ Supports the immune system – Contains lymphatic tissue that fights infections.
💡 Interesting Fact:
Some people live perfectly fine without an appendix, but research suggests it helps prevent certain digestive diseases.
5. The Thymus: The Immune System’s Training Ground
Your thymus may not be well known, but it’s critical in building your body’s defense system!
What the Thymus Does
🛡️ Trains immune cells – Produces T-cells, which help fight off viruses and infections.
📉 Shrinks with age – Your thymus is most active in childhood and gradually shrinks over time.
👶 Did You Know?
By the time you reach puberty, your thymus begins shrinking—eventually, it becomes mostly fat tissue!
6. The Pineal Gland: The Sleep Regulator
Ever felt tired at night and awake in the morning? You can thank your pineal gland for that!
Functions of the Pineal Gland
🌙 Produces melatonin – Controls your sleep-wake cycle.
🌓 Responds to light – Releases more melatonin at night and less during the day.
💡 Pro Sleep Tip:
Avoid blue light (from phones and screens) at night—it disrupts your pineal gland and makes falling asleep harder!
These often-overlooked body parts may not be as famous as your heart or lungs, but they play crucial roles in keeping you alive and well!
How the Body Adapts to Change and Challenges
Your body is an incredible machine, constantly adapting to changes, injuries, and environmental shifts. Whether it’s healing wounds, adjusting to extreme temperatures, or aging gracefully, your body has built-in survival mechanisms that help it thrive.
Let’s explore some of the most fascinating ways your body adapts!
1. The Body’s Healing Powers: How Injuries Repair Themselves
Have you ever gotten a cut or scrape, only to see it magically heal a few days later? That’s your body’s self-repair system in action!
Stages of Wound Healing
1️⃣ Inflammation – Your immune system sends white blood cells to fight infection and clean the wound.
2️⃣ Clotting – Platelets form a scab to stop bleeding.
3️⃣ Regeneration – New skin cells replace damaged ones.
4️⃣ Remodeling – The skin strengthens, sometimes leaving a scar.
🩹 Pro Tip:
Eating vitamin C-rich foods (like oranges and bell peppers) can speed up wound healing!
2. Muscle Growth: How Your Body Gets Stronger 💪
Ever wonder why lifting weights makes your muscles bigger and stronger? Your body adapts to stress by rebuilding muscle fibers thicker than before!
How Muscle Growth Works
🏋️♂️ Exercise – Strength training damages muscle fibers (in a good way!).
🥩 Protein Intake – Your body uses protein to rebuild the damaged fibers.
💤 Rest & Recovery – Muscles grow during rest, not while exercising!
💡 Did You Know?
Your muscles start shrinking within two weeks of inactivity—so keep moving!
3. The Brain’s Plasticity: How You Keep Learning 🧠
Your brain isn’t fixed—it’s constantly rewiring itself! This is called neuroplasticity, and it allows you to learn new skills, recover from injuries, and adapt to new environments.
Ways to Boost Brain Adaptation
📖 Lifelong Learning – Reading, puzzles, and learning new languages keep your brain sharp.
🏃♂️ Exercise – Physical activity increases blood flow to the brain, helping memory.
🥑 Healthy Diet – Omega-3s (found in avocados and salmon) improve brain function.
💡 Brain Fact:
Taxi drivers in London have larger hippocampi (the memory center of the brain) because they memorize so many streets!
4. How Your Body Adjusts to Extreme Temperatures 🌡️
Ever felt your body sweat in the heat or shiver in the cold? That’s your built-in temperature regulation system at work!
How Your Body Cools Down ☀️
💦 Sweating – Your sweat evaporates, cooling your skin.
🌬️ Increased Blood Flow – Your blood vessels expand, releasing heat.
How Your Body Warms Up ❄️
🥶 Shivering – Tiny muscle contractions create heat.
🩸 Vasoconstriction – Blood vessels narrow to keep warmth inside.
💡 Survival Fact:
If you stay in a cold environment for weeks, your body produces more brown fat, which generates heat to keep you warm!
5. Aging: How Your Body Evolves Over Time ⏳
Aging is natural, but your body adapts in surprising ways to help you stay strong and healthy!
How the Body Adapts to Aging
Bones become denser in youth but may weaken over time—weight-bearing exercises help!
Metabolism slows down, so eating nutrient-dense foods is key.
The brain remains plastic, meaning you can keep learning at any age.
🧑⚕️ Healthy Aging Tip:
Regular exercise, hydration, and a balanced diet can slow many effects of aging!
Your body is a master of adaptation—whether it’s healing, growing, or adjusting to new conditions, it never stops working to keep you at your best!
The Five Senses – How We Perceive the World
Your body is packed with incredible sensory organs that help you see, hear, touch, taste, and smell the world around you. These five senses work together like a highly coordinated orchestra, constantly sending information to your brain, so you can navigate daily life effortlessly.
Let’s dive into how each of your senses functions and some fascinating facts about them!
1. Sight – The Power of Vision 👀
Your eyes are complex optical devices, allowing you to process light and color in real time. Nearly 80% of what you perceive comes from your sense of sight!
How Vision Works
1️⃣ Light enters through the cornea and pupil.
2️⃣ The lens focuses light onto the retina.
3️⃣ Photoreceptors (rods and cones) convert light into electrical signals.
4️⃣ The optic nerve sends signals to the brain, forming an image.
Fun Eye Facts
👁️ The human eye can distinguish about 10 million colors!
🌌 At night, your eyes become more sensitive to blue light to improve night vision.
👶 Babies are born colorblind—they develop full-color vision over time.
💡 Eye Health Tip:
Eating carrots and leafy greens supports retinal health and prevents vision loss.
2. Hearing – The Sound Decoder 🎧
Your ears don’t just help you hear—they also play a crucial role in balance!
How Hearing Works
1️⃣ Sound waves enter through the outer ear.
2️⃣ Vibrations pass through the eardrum and tiny ear bones.
3️⃣ The cochlea (a snail-shaped organ) converts vibrations into nerve signals.
4️⃣ The auditory nerve sends signals to the brain, where they’re processed as sound.
Amazing Hearing Facts
👂 Your ears never stop hearing—even when you sleep, your brain just tunes out noises.
🐋 Humans can hear sounds from 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz, but whales communicate at frequencies beyond our hearing range!
👶 Babies are born with fully developed hearing and can recognize their mother’s voice right after birth!
🎵 Hearing Health Tip:
Listening to loud music over 85 decibels for long periods can damage hearing—keep the volume at a safe level!
3. Touch – The Most Immediate Sense ✋
Your skin is covered in millions of nerve endings, making touch the fastest-reacting sense in the human body!
How the Sense of Touch Works
🖐️ Receptors in the skin detect pressure, texture, pain, and temperature.
⚡ Nerve signals travel instantly to the brain through the spinal cord.
🧠 The brain processes sensations—like softness, heat, or pain—allowing you to react.
Incredible Touch Facts
⚡ Your brain processes touch sensations in less than 0.01 seconds!
👣 Your feet have more sensory nerve endings than most other body parts—helping with balance and movement.
🔥 Some people have a rare condition called congenital insensitivity to pain, where they can’t feel pain at all!
🖐️ Touch Sensitivity Tip:
Regular massage therapy can improve circulation, relaxation, and even immune function!
4. Taste – The Flavor Detective 👅
Your tongue is covered in thousands of taste buds that allow you to experience flavors.
How Taste Works
1️⃣ Food molecules dissolve in saliva and enter the taste buds.
2️⃣ Taste receptors detect sweet, sour, salty, bitter, and umami (savory) flavors.
3️⃣ The gustatory nerve sends signals to the brain, identifying the taste.
Fun Facts About Taste
🍫 The tongue map is a myth—all taste buds can detect every flavor!
🌶️ Spicy foods don’t activate taste buds—they trigger pain receptors!
👅 Your sense of taste weakens with age, which is why older people prefer stronger flavors.
👄 Taste Boosting Tip:
Drinking plenty of water enhances taste perception—dehydration can dull your sense of taste!
5. Smell – The Emotion Trigger 👃
Your nose can detect over a trillion different scents, and smell is closely linked to memory and emotions!
How Smell Works
1️⃣ Airborne odor molecules enter the nasal cavity.
2️⃣ Olfactory receptors detect the scent and send signals to the olfactory bulb.
3️⃣ The brain identifies the smell and links it to memories and emotions.
Fascinating Smell Facts
👃 Women have a stronger sense of smell than men!
🧠 Your olfactory bulb is connected to the part of your brain that stores memories—that’s why certain scents trigger nostalgia!
🐕 Dogs have 40 times more olfactory receptors than humans, making their sense of smell far superior.
🌿 Smell Enhancement Tip:
Practicing deep breathing exercises can help sharpen your sense of smell!
Your five senses work together in amazing ways, shaping how you experience the world!
FAQs
Can You Live Without Certain Organs?
Yes! The human body is surprisingly resilient and can function without several organs. Here are some organs you can live without:
Appendix – Once thought useless, it helps with gut bacteria but isn’t essential.
Gallbladder – Helps digest fat, but your liver can handle the job without it.
One Kidney – You can survive with just one fully functioning kidney.
Spleen – It fights infections, but other organs (like the liver and lymph nodes) take over if it’s removed.
💡 Fun Fact: Some people are born with just one lung, and their body compensates by making the single lung grow larger!
Why Do We Get Goosebumps?
Goosebumps are a survival instinct from our ancestors! When you’re cold or scared, tiny muscles in your skin contract, making hair stand up. This used to help trap warmth or make early humans look bigger to scare off predators.
🐱 Similar to animals: Ever seen a cat’s fur puff up when it’s scared? That’s the same reflex at work!
Why Do Fingers Wrinkle in Water?
Your fingers wrinkle after being in water for a long time due to an automatic response from your nervous system.
🌊 Scientists believe it helps improve grip in wet conditions—like tire treads on a car!
💡 Interesting Fact: This only happens in fingers and toes because they have a higher concentration of nerve endings.
Why Do We Get Brain Freeze?
Ever eaten ice cream too fast and felt a sharp headache? That’s brain freeze!
🍦 When something cold touches the roof of your mouth, it triggers blood vessels in your head to tighten and expand quickly, causing a short painful sensation.
🧊 Quick Fix: Press your tongue against the roof of your mouth to warm it up and stop the pain!
Conclusion
The human body is a remarkable masterpiece, working tirelessly to keep us alive and thriving. From the beating heart to the intricate nervous system, every part plays a crucial role in maintaining balance, function, and survival.
By understanding how our organs, senses, and body systems work together, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and resilience of the human form. Whether it’s the brain’s adaptability, the skin’s ability to heal, or the heart’s relentless pumping, our bodies are nothing short of extraordinary.
To keep this incredible system running at its best, it’s essential to nourish, move, and care for it. Your body is the only place you have to live—so treat it well, stay curious, and continue exploring the wonders within! 🚀💙

